SDK Mobile Integration Guide
This document provides technical guidance for the integration of the Halo.SDK into a host Android application.
| The Halo Dot SDK is an Isolating MPoC SDK payment processing software with Attestation & Monitoring Capabilities. |
|---|
| The architecture of this isolating MPoC Payment Software is described in the diagram below. The diagram also showcases the SDK boundary and the interaction between the SDK, its integrating channels, and the party payment gateways. It includes details of how data is sent in-between the boundary. |
| Inside: Halo.SDK code + SDK-managed cryptographic material; SDK-managed secure channels (to A&M and external devices where applicable); SDK-managed TUI for PIN. |
| Outside: Host MPoC Application code, UI, and business logic; device NFC interface and touchscreen (as interfaces, not part of SDK); third-party payment host(s). |
| Account-data input paths: COTS-native NFC → SDK; PIN via SDK TUI → SDK. |
| Control/attestation signals: SDK ⇄ A&M back end; SDK → host app (callbacks) without exposing sensitive assets. |
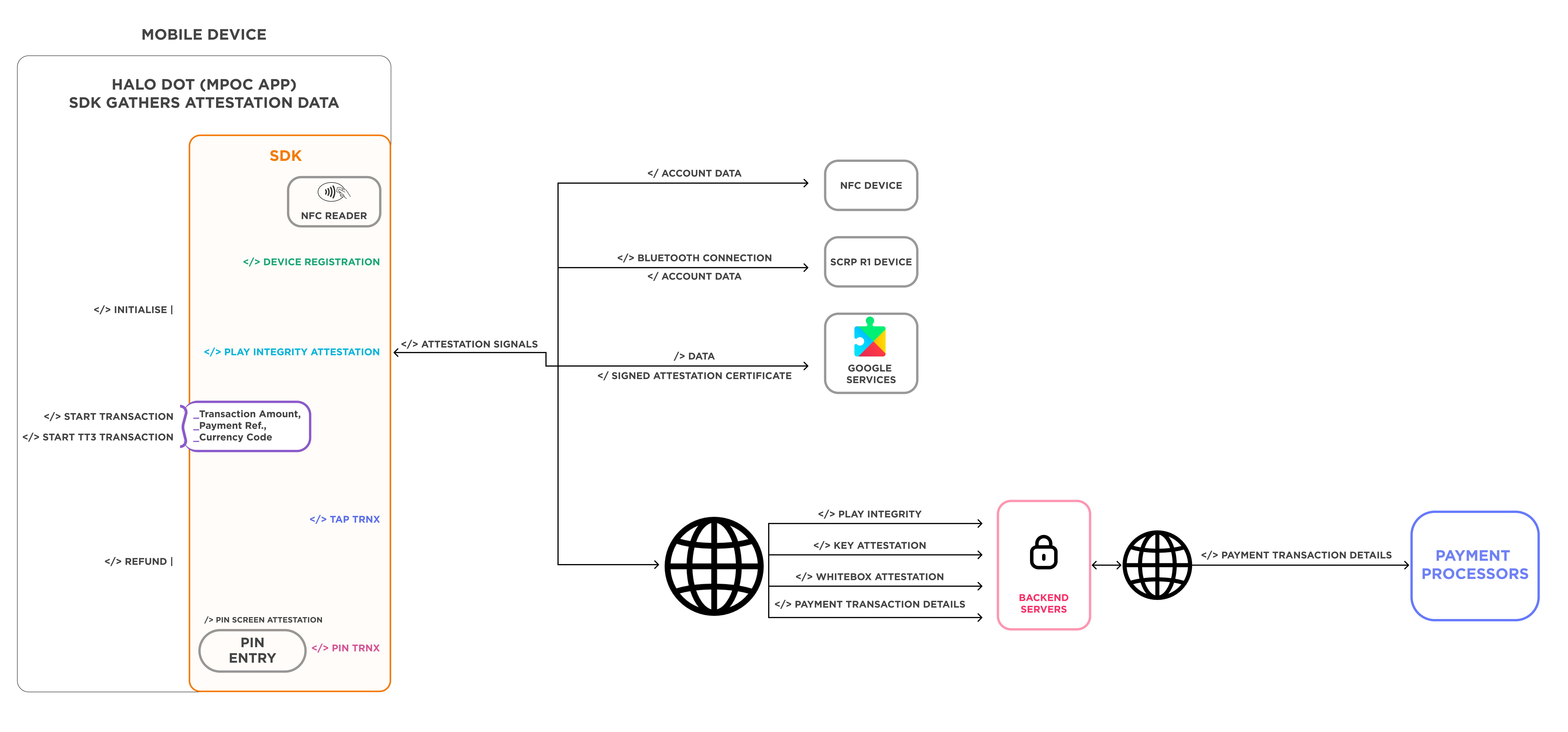
SDK Boundary
The Halo.SDK is an isolated system development kit with A&M functionality. It operates in an isolated memory space, which provides sufficient separation of data processing between the SDK and other software (including the integrating app). The MPoC Application cannot access the SDK's memory or sensitive assets (including cryptographic keys and plaintext account/PIN data). This aligns with the MPoC definition of an Isolating SDK; any access would indicate non-compliant integration.
Detailed SDK Boundary Description
Inside the SDK boundary:
- SDK code and data, including SDK-managed cryptographic material, including the white-box.
- EMV kernel and payment processing logic which handles account data in the SDK.
- SDK-managed secure channels (to A&M and external devices where applicable).
- SDK-managed Trusted User Interface (TUI) for PIN entry.
Outside the SDK boundary:
- Host MPoC Application code, UI, and business logic.
- Device NFC interface and touchscreen (as interfaces, not part of SDK).
- Third-party payment providers which transactions are routed to.
Account-data input paths:
- COTS-native NFC → SDK: Contactless PAN/EMV data enters via the device NFC interface and is processed within the SDK.
- PIN via SDK TUI → SDK: PIN entry is handled by the SDK's TUI, ensuring that the host app cannot access the PIN.
A&M and attestation signals:
- SDK ⇄ A&M back end: The SDK communicates with the A&M backend for attestation and monitoring over secure channels.
- SDK → host app (callbacks) without exposing sensitive assets: The SDK provides callbacks to the host app for status updates and errors, but does not expose sensitive data.
The Halo.SDK does not output plaintext PAN, PIN or any internal keys. Allowed outputs included a masked PAN (e.g. maskedPAN: 518103******3425 - from the HaloTransactionResult example included in this guide), and transaction status codes. The SDK does not expose any sensitive data to the host app, ensuring compliance with MPoC requirements.
Security Guidance for Integrators
This section provides mandatory security guidance for integrators of the Halo.SDK. It supplements the functional integration instructions in this document by explicitly defining security requirements, prohibitions, and responsibilities. Failure to follow these requirements may result in failed attestation, blocked terminals, or loss of compliance with PCI MPoC.
General Do’s
- Always use server-issued JWTs: The app must obtain fresh JWTs from its backend.
- Keep JWT lifetime short: The recommended maximum is 15 minutes.
- Propagate SDK security callbacks: The integrator app must always handle
onSecurityErrorandonAttestationErrorby alerting the merchant. - Use official SDK builds only: Integrators must only use Halo-provided, signed AAR packages.
- Enforce SDK lifecycle hooks: Ensure all required
onCreate,onStart,onResume, etc. methods are properly wired. - Update regularly: Always integrate the latest SDK release as soon as published by Halo.
General Don’ts
- Do not store or cache JWTs in local storage, logs, or other persistent locations.
- Do not hardcode JWTs or keys into the application package.
- Do not attempt to modify or override the SDK’s Trusted User Interface for PIN entry.
- Do not attempt to intercept or alter SDK API calls related to security checks (root detection, attestation, debug/instrumentation detection).
- Do not silence, suppress, or replace SDK tamper notifications (e.g. “RootedDevice” or “DebuggedDevice”).
- Do not attempt to use the SDK on unsupported platforms (see Supported Platforms section).
Platform & OS Dependencies
- The Halo.SDK relies on the host Android OS security model (application sandboxing, permissions, and secure process isolation).
- The SDK requires Google Play Integrity attestation services to function; devices where this service is unavailable will fail initialization and attestation.
- The SDK requires that developer options be disabled, and that no accessibility services are active during PIN entry for its release builds. Debug builds may allow these for testing purposes only but will not be permitted in production.
- Integrators must ensure that apps request and retain the following permissions:
INTERNETCAMERANFCBLUETOOTH_SCANBLUETOOTH_CONNECTACCESS_FINE_LOCATIONorACCESS_COARSE_LOCATION(if using Android 11 and below)
- Integrators must allow network egress to
kernelserver.<client>.<prod|dev|qa>.haloplus.iofor both A&M and transaction processing.
Secure Update Process
- Halo publishes AAR builds of the SDK on a monthly basis.
- Integrators must not modify SDK binaries.
- Each new SDK release contains security patches; integrators are required to upgrade within 30 days of release to remain compliant.
- Updating the SDK requires full regression testing of app flows to ensure lifecycle and attestation processes remain intact.
SDK Distribution and Access Control
- The Halo SDK AAR is published in a private Maven repository backed by Amazon S3.
- Halo issues per‑customer, long‑lived read‑only IAM credentials scoped to the specific SDK bucket/prefix. Credentials must not be shared between customers.
- Repository hygiene: S3 Versioning is enabled; pulls/reads are audit‑logged so access can be traced by Halo operations.
- Integrator obligations:
- Retrieve the SDK only using the customer‑specific credentials issued by Halo.
- Do not mirror/redistribute Halo artifacts publicly.
- Track Halo release notifications and plan regular updates; Halo may enforce minimum SDK versions (see Rollout & gating).
- Authenticity is enforced at the application layer: all MPoC Applications are signed; authenticity and integrity are further validated by remote attestation using embedded certificates signed by Halo’s HSM‑backed CA (protected via obfuscation).
EMV kernel data & configuration
- Authoritative storage: maintained in Halo’s backend database; host apps cannot alter these values.
- Change requests: initiated by integrator or payment processor but executed only by Halo administrators via a restricted administrative API. Every admin uses an individual account; all actions are audit‑logged.
- Promotion flow: each change is tested in UAT and, once approved, promoted to production.
- Delivery to devices: after successful attestation, the SDK retrieves and atomically applies the current kernel/config. Partial/failed updates are not applied; errors are surfaced via the intialization result response and the SDK remains in a safe state.
A&M policy/configuration
- Operated solely by Halo; integrators do not configure or operate A&M.
- Attestation configuration resides only on the backend. The SDK does not receive attestation policy/config before attestation. Attestation is performed against backend policy over SDK‑managed secure channels.
- If attestation/policy is not satisfied, the SDK transactions are not permitted.
**Certificate pin sets used in JWTs (base64 SHA-256)
- JWTs include a base64 SHA‑256 fingerprint list pinning to the TLS key used by the Halo kernel server.
- Automatic rotation: Production (and other environment) certificates/keys are rotated automatically by Halo DevOps on AWS. Halo notifies customers of upcoming changes and provides overlapping fingerprints to support migration. Integrators must update their JWT pin sets by the communicated effective‑by date.
Device prerequisites for config updates
- Accurate device time (significant drift will cause attestation failure).
- Network egress to
kernelserver.<client>.<prod|dev|qa>.haloplus.io. - Healthy initialization/attestation state.
Rollout & gating
- Halo may enforce a minimum SDK version (via versioned SDK↔kernel endpoints). Devices below the minimum may be refused by attestation/policy until updated.
- Debug builds of the Halo SDK are not usable in production.
Software-Protected Cryptography Update Cadence
Public (Integrator‑facing)
- Halo employs software‑protected cryptography to protect embedded secrets.
- Recommended cadence: Halo strongly recommends updating to new SDK releases as they carry a refreshed white‑box approximately every 30 days. Halo publishes availability dates in the release notes and notifies customers of updates.
- Operational behavior: The SDK continues to attest and transact when policy permits; however, older releases may expose increased risk. Integrators choosing to delay updates accept the risk to their merchant UX and security posture.
- No epoch enforcement: Halo does not currently enforce a hard Epoch ID cutoff. Minimum SDK version enforcement may still apply (see Rollout & gating in 1G‑1.5).
Evidence & audit
- Release notes record availability dates for each updated white‑box build.
- Backend policy decisions and attestation outcomes are audit‑logged per Halo policy.
Tamper & Security Event Handling
- When the SDK reports RootedDevice, InstrumentedDevice, or DebuggedDevice, the host application must immediately display a clear message to the merchant that the device is not secure and transactions are disabled.
- Example message (recommended):
“⚠️ This device has been tampered with and is not permitted to process payments. Please use a secure device.”
- Merchants must not be allowed to override or bypass this error.
- The host application must log these events (without sensitive data) for operational monitoring.
Supported Platforms
- The Halo.SDK is certified for COTS-native NFC Android devices that support Google Play Integrity API.
- The SDK is not supported on rooted, emulated, or debugged environments.
- The SDK is only supported on devices running Android 10 (API level 29) and above.
- The SDK will only work on devices with Google Play Services installed and an accurate system clock.
- The SDK currently supports the following SCRP device:
- WiseEasy R1 FC (Bluetooth)
Key Management Responsibilities
- JWT signing keys must be securely generated and managed by the integrator’s backend.
- Public keys must be provisioned to Halo in advance, and certificate rotation must follow Halo’s published schedule.
- Integrators must not generate or manage cryptographic keys within the mobile app.
- Halo manages all SDK-embedded keys and secrets, including white-box cryptography, within the SDK binary.
- Here is a more detailed outline of all the cryptographic assets and how they are managed: Cryptographic Assets, Key Management Policy
1. Remote Attestation of the App by the Halo Backend
In accordance with prescribed security requirements, the Halo backend performs remote attestation of the integrating app using Google’s Play Integrity attestation framework.
App Values Required by Halo Server for Remote Attestation
The following attestation payload fields must be configured in the Halo backend with each release of the integrating app so that they can be checked by the backend during remote attestation.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| applicationName | The name of the app e.g. "Halo.Dot Go" |
| apkPackageName | The application id or package name e.g. za.co.synthesis.halo.mpos.go |
| apkCertificateDigestSha256 | The base64 encoded SHA-256 hash of the certificate used to sign the integrating app |
| applicationVersion | The version number of the integrating app |
| registeredAppInstaller | The application id or package name of the app that will be used to install the integrating app e.g. com.android.packageinstaller |
These details will need to be communicated to the Halo team so that they can be configured in the Halo backend.
Attestation and Monitoring Model
Halo operates the Attestation & Monitoring (A&M) service as part of the Halo MPoC Software. Third-party operation of A&M is not supported. The content below is provided so integrators and assessment laboratories can understand and validate correct A&M operation for MPoC evaluation.
A&M Operations Model
Halo is the sole operator of the A&M component. Integrators do not deploy, configure, or operate A&M.
A&M Operations Guidance
Base configuration
- Endpoints. The SDK uses the Halo backend kernel server for both A&M and transaction processing:
kernelserver.<client>.<prod|dev|qa>.haloplus.io. - Certificate pinning. A base64 SHA-256 certificate fingerprint of the kernel server must be configured (provided by Halo per environment; it can also be derived from the server TLS certificate).
- Time source. Devices must not have significant clock drift; otherwise the Halo SDK will fail attestation.
Deployment posture
- Builds. Debug builds of the Halo SDK are not usable in production (restricted to QA/Dev environments).
- Secrets. The SDK manages its own secrets internally. For all environments, the integrator’s JWT signing public key must be provisioned to Halo.
- TLS & JWT pin set. TLS is enforced in all our environments; the JWT must include the base64 SHA-256 fingerprint(s) for the kernel server (supporting certificate rotation).
Runtime behavior
- Cadence. After the first initialization, the Halo SDK performs attestation every 5 minutes, and also before each transaction.
- Callbacks. Any failures are delivered via
IHaloCallbacks.onSecurityErrorandIHaloCallbacks.onAttestationError. - Fail-closed. If attestation fails, no transactions are permitted by the SDK.
Configuration surface
- Integrator-provided values (per app release):
- Application name and application ID (package name).
- Base64 SHA-256 digest of the signing certificate used for the app.
- Installer application ID (e.g., MDM package name if app is deployed via MDM).
- Mandatory checks performed by the SDK/A&M (not configurable): OS version; device model; installation source; attestation nonce; device key hash; application ID; OS rollback status; hardware-backed signal checks; profile checks; application recognition; Google Play license checks.
Operations procedures
- For assessment labs, here are links to Halo’s internal policies (logging, rollout, incident response).
- All documents have authors and a log of changes. The logging document outlines our full logging and monitoring approach. The rollout document outlines our release and promotion process. The incident response document outlines our incident response plan.
Integrator Obligations (read-only responsibilities)
- No A&M API surface. The integrating app does not call A&M APIs; the SDK invokes A&M during initialization, periodically (5-minute cadence), and before each transaction. Attestation cannot be avoided.
- Network egress. Allow egress to the kernel server for both A&M and transaction processing. Because the same endpoint provides both, integrators cannot choose transactions without A&M.
- Terminal handling. Treat any attestation/security error as terminal for payment flows; the SDK will block transactions in these states.
- Configuration control. Attestation configuration is not modifiable by the integrating app or its backend.
2. Requirements of the Integrating App’s Backend
JWT
All calls made to the Halo.SDK require a valid JSON Web Token. The integrating app’s backend is expected to supply the integrating app with a JWT that can be used to authenticate with the Halo backend. The SDK provides an interface for a function, onRequestJWT(callback: (String) -> Unit), that it will call whenever a JWT is required.
An asymmetric key is used so that the JWT can be issued (signed) by one system (integrating app server), and independently verified by another (Halo backend).
JWT Lifetime
Since the JWT effectively authorizes payment acceptance for a given merchant user, its lifetime should be kept as short as possible to minimize the window of opportunity for an attacker to compromise the token and to limit the potential impact in the event of a breach.
A lifetime of 15 minutes is recommended.
JWT Signing Public Key Format
The JWT public key should be published as a certificate in a text-friendly format, e.g., Base64 encoded PEM (.crt, .pem).
JWT Serialization Format
The compact serialization format is expected, i.e.:
urlencodedB64(header) + '.' + urlencodedB64(payload) + '.' + urlencodedB64(signature)
For example:
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJsb2dnZWRJbkFzIjoiYWRtaW4iLCJpYXQiOjE0MjI3Nzk2Mzh9.gzSraSYS8EXBxLN_oWnFSRgCzcmJmMjLiuyu5CSpyH
JWT Claims
The JWT must contain a number of claims:
| Field | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| alg | String | The signing algorithm is RSA signed SHA-256 hash, aliased as RS256. An asymmetric encryption (signing) scheme is required to allow the Kernel Server to validate the token without being able to generate it. If symmetric key encryption was used to sign the auth token (e.g., using the HMAC algorithm), then non-repudiation would be lost. |
| sub | String | The Payment Processor Merchant-User ID. |
| iss | String | A unique identifier for the JWT issuer, agreed upon by the JWT issuer and Halo, and configured in advance by Halo in the backend, e.g., authserver.haloplus.io. |
| aud | String | The fully qualified domain name of the Halo Kernel server e.g., 'kernelserver.qa.haloplus.io'. This value should be obtained from Halo (different per customer environment). |
| usr | String | The details of the user performing the transaction, typically the username used to sign into the integrator app. |
| iat | NumericDate | The UTC timestamp of when the JWT was generated. |
| exp | NumericDate | The UTC time of expiration of the JWT. |
| x-tid | String | The terminal identifier to be used for transactions (if available). |
| aud_fingerprints | String | A CSV list of expected SHA-256 fingerprints for the Halo Kernel server. This list may contain multiple values to support certificate rotation. In the QA environment, the expected value as of writing this would be: "sha256/CNOtjib4NAlSqDZDY5aknDcVbcfLEWBgnGl/dgec4aA=". |
| x-custom-claims | String | A JSON object with keys and values that are strings for custom claims used in your integration. This is custom and should be arranged with the Halo team before use and is optional as well. |
If using the Halo Dot Adaptor, the following additional fields are required
| Field | Type | Note |
|---|---|---|
| x-am-endpoint | String | URL of Halo A&M endpoint, e.g., 'kernelserver.qa.haloplus.io'. |
| x-am-endpoint-fingerprints | String | A CSV list of expected SHA-256 fingerprints for the A&M endpoint. This list may contain multiple values to support certificate rotation. In the QA environment, the expected value as of writing this would be: "sha256/CNOtjib4NAlSqDZDY5aknDcVbcfLEWBgnGl/dgec4aA=". |
All these values can be validated by making a POST request to https://kernelserver.qa.haloplus.io/tokens/checkjwt. Your JWT should be added as a header (Bearer Auth).
3. SDK Binary
The Halo.SDK is written in Kotlin and packaged as an AAR (Android Archive Library). For security reasons, the compiled binary has been obfuscated.
See the Getting Started Guide for a detailed guide on accessing and getting started with the SDK.
4. Application Manifest
The AndroidManifest.xml application manifest file of the mobile app must include the following user permissions:
android.permission.INTERNET– call out to the backend over the internet.android.permission.CAMERA– to prevent third-party apps from using the camera to capture card data.android.permission.NFC– use the NFC module.android.permission.BLUETOOTH_SCAN– Bluetooth scan permissions.*android.permission.BLUETOOTH_CONNECT– Bluetooth connect permissions.*
In addition, to indicate to the Google Play store that this is an NFC-enabled app, the android.hardware.nfc feature needs to be specified with required=false. If required is set to true, then the mobile app itself will not be allowed to be installed on devices that don’t support NFC, which is presumed to not be the desired behavior.
5. Life-Cycle Methods
In order for the SDK to properly handle the Android application life cycle the host app needs to add hooks into the following Android lifecycle methods on the MainActivity or relevant activity classes.
⚠️ Do not hook up to a sub-activity or a fragment as this will cause problems. If you do so, please use our multi-activity test app as a reference. Test App Source
List of Android lifecycle methods:
onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState, PersistableBundle persistentState)onStart()onResume()onPause()onStop()onSaveInstanceState(Bundle outState, PersistableBundle outPersistentState)onSaveInstanceState(Bundle outState)onDestroy()
Halo.SDK has corresponding static methods with matching method signatures for each of the Android lifecycle methods.
This can all be wired up as follows:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState, PersistableBundle persistentState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState, persistentState);
// your mobile app code here
HaloSDK.onCreate(this, this, savedInstanceState, persistentState);
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
// your mobile app code here
HaloSDK.onStart();
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
// your mobile app code here
HaloSDK.onResume();
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
// your mobile app code here
HaloSDK.onPause();
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
// your mobile app code here
HaloSDK.onStop();
}
@Override
public void onSaveInstanceState(@NonNull Bundle outState, @NonNull PersistableBundle outPersistentState) {
super.onSaveInstanceState(outState, outPersistentState);
// your mobile app code here
HaloSDK.onSaveInstanceState(outState, outPersistentState);
}
@Override
protected void onSaveInstanceState(@NonNull Bundle outState) {
super.onSaveInstanceState(outState);
// your mobile app code here
HaloSDK.onSaveInstanceState(outState);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
// your mobile app code here
HaloSDK.onDestroy();
}
}
6. Initialization of the SDK
Separate from the lifecycle hooks, the Halo.SDK must be initialized before any transaction by calling the static initialize method on the SDK and passing a HaloInitializationParameters instance as an argument. It is sufficient and recommended to call initialize once per user session.
The SDK will attempt to perform the following sequence of actions:
- Perform runtime checks (checking if device is not rooted, running in debug mode, or under instrumentation)
- Confirm that the software (Android version) and hardware platform (NFC device) is sufficient
- Connect to the server and pass the JWT for verification
- Confirm that the device has been enrolled and is not blocked; otherwise re-enroll if necessary
- Perform device-local Google Play Integrity key attestation actions, and submit results to the server for remote verification
- Retrieve terminal configuration from the server
- Initialize the SDK to a state where it will accept transactions
The result will be communicated, typically asynchronously, to the host application via invoking the callback registered in IHaloCallbacks.onInitializationResult and passing a HaloInitializationResult instance.
The HaloInitializationResult.resultType field indicates whether or not the initialization was successful or not. A value Initialized indicates success, all other values indicate some kind of failure.
In the case of failure, the errorCode field may hold more information, whereas in the case of success, the SDK is now ready to accept a transaction.
HaloInitializationParameters
import za.co.synthesis.halo.sdk.model.HaloInitializationParameters
public class HaloInitializationParameters {
public IHaloCallbacks haloCallBacks;
public Long cardTimeTimeoutMS;
public String applicationName;
public String applicationVersion;
}
Long cardTimeTimeoutMS - Timeout value, in milliseconds, that the SDK will wait for a card tap after startTransaction has been called, before returning with a timeout error.
String applicationName - The fully qualified package name of the calling application.
String applicationVersion - The version number of the calling application.
IHaloCallbacks haloCallBacks - See below discussion on the IHaloCallbacks interface.
IHaloCallbacks
import za.co.synthesis.halo.sdk.model.IHaloCallbacks
public interface IHaloCallbacks {
void onInitializationResult(HaloInitializationResult result);
void onHaloUIMessage(HaloUIMessage message);
void onHaloTransactionResult(HaloTransactionResult result);
void onRequestJWT(Function1<? super String, Unit> function1);
void onAttestationError(HaloAttestationHealthResult result);
void onSecurityError(HaloErrorCode code);
void onCameraControlLost();
}
The IHaloCallbacks interface encapsulates the call-back methods that the HaloSDK will use to asynchronously communicate back to the host application at relevant junctures:
- The outcome of the initialization process (
onInitializationResult) - Interim transaction progress (
onHaloUIMessage) - Final outcome of a transaction (
onHaloTransactionResult) - Issues with intermittent attestation checks (
onAttestationError) - Security violation detected (rooting, debugging, integrity) (
onSecurityError)
HaloInitializationResult
import za.co.synthesis.halo.sdk.model.HaloInitializationResult
public class HaloInitializationResult {
public HaloInitializationResultType resultType;
public Currency terminalCurrency;
public List<String> terminalLanguageCodes;
public String terminalCountryCode;
public String message;
}
Notes on HaloInitializationResult:
-
HaloInitializationResultTypeHere is a list of possible values for
HaloInitializationResultTypeValue Meaning AuthenticationError Error occurred during authentication AttestationFailure Attestation failed AttestationSystemNotInitialised Initialization failed because attestation system is not initialised CameraPermissionNotGranted No camera permission ConfigFetchError Unable to fetch terminal config DebuggedDevice Debug mode detected GeneralError General failure HttpClientError Unable to open web connection Initialized Success InitializedWithoutConfigs Success status (without using terminal configs) InstrumentedDevice Runtime instrumentation detected NetworkError Network socket error during connection to server NFCDisabledError NFC either absent, turned off, or NFC permission not granted NoAppContext App context is null - Did you call onCreate()? NoTerminalContainer TerminalContainer is null - did you call onCreate()? RemoteAttestationFailure Device failed remote leg of Android Play Integrity attestation RootedDevice Device rooting detected TEEAttestationFailure TEE attestation failed UnableToConfigureTerminal Error occurred configuring terminal UnsupportedDevice The current device is unsupported - usually due to NFC UnsupportedOperatingSystemVersion Android OS too low -
Terminal Localisation Information Returned in
HaloInitializationResultAs part of initialization, the SDK will fetch its pre-defined terminal configuration from the Halo server and this includes localization data which should be checked by the host application to ensure that the terminal is transacting in the expected currency which is required for the limit checks done as part of kernel processing to be performed in the correct matching currency. In addition, these values should be used to determine the correct currency symbol and a number of decimal points to use when displaying the transaction amount to the cardholder.
-
terminalLanguageCodesThe EMV terminal specification dictates that the terminal be configured with a list of language preferences (ISO 639-1 alpha2 language code), ordered from highest to lowest priority. The mobile app should ideally use this list to determine which language to use for display purposes.
-
terminalCurrencyThe terminal has a single supported currency. This is the currency in which card risk limits are configured, and the transaction must be conducted. It is also the currency that must be used when displaying amounts. The mobile app should determine the correct currency symbol and a number of decimal places from this. If this value is not as expected, then the mobile app should not allow transactions.
-
terminalCountryCodeThe terminal is configured with a country code that indicates the domestic country. The returned value is formatted as an ISO 3166-1 numeric 3 country code left padded with zeros to length 4, e.g. 0710 = South Africa.
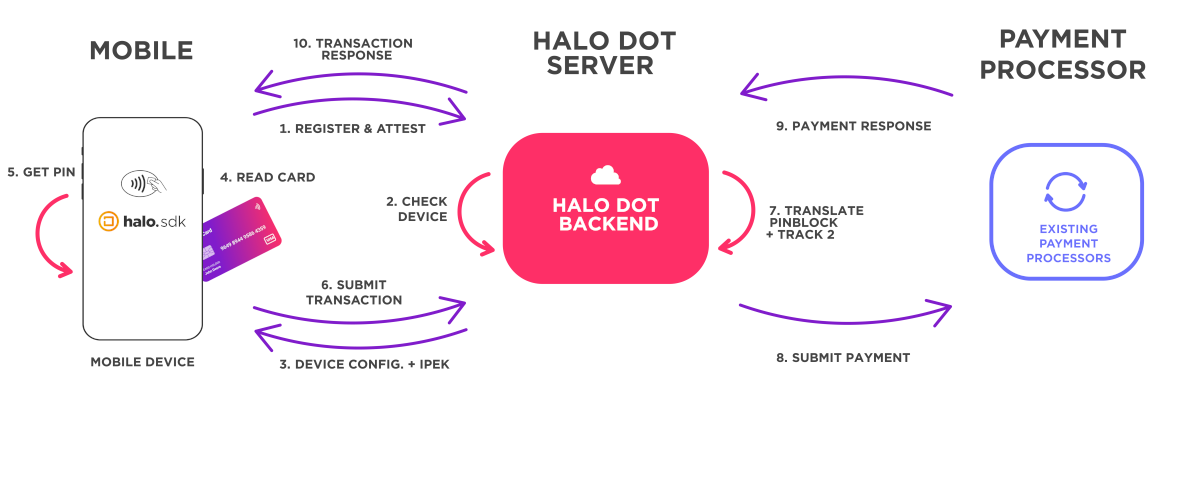
7. Transaction Flow
This section describes the SDK transaction flow in more detail.
HaloSDK.startTransaction
Once the SDK has been successfully initialized, as indicated by a HaloInitializationResultType of Initialized, a transaction may be initiated by calling HaloSDK.startTransaction.
public final fun startTransaction(
transactionAmount: BigDecimal,
merchantTransactionReference: String
currencyCode: String? = null,
extraReceiptFields: Map<String, String>? = null,
passthroughFields: JSONObject? = null,
transactionType: TransactionType = TransactionType.Purchase
): za.co.synthesis.halo.sdk.model.HaloStartTransactionResult
Let's take a closer look at startTransaction parameters:
transactionAmount- The purchase amount, stated in theterminalCurrencyas returned inHaloInitializationResult.terminalCurrency.merchantTransactionReference- It is recommended to use a random GUID for this purpose.currencyCode- The terminal currency code if different from theterminalCurrencyreturned inHaloInitializationResult.terminalCurrency. If not specified, the terminal currency will be used.extraReceiptFields- A map of additional fields that will be included in the EMV receipt. This is optional and can be used to include additional information on the receipt, such as customer details or order numbers.passthroughFields- A JSON object containing additional fields that will be passed through to the payment processor. This is optional and can be used to include additional information that the payment processor may require.transactionType- The type of transaction that will be done - which could either be a Purchase, Cash, PurchaseWithCashback or Refund.
The merchantTransactionReference is a unique-per-merchant transaction reference generated and supplied by the integrating app. Halo will generate and maintain its own internal ID for the transaction (haloTransactionReference), but from the perspective of the integrating app merchantTransactionReference together with the value Payment Processor Merchant-User ID specified in the JWT sub field can be used to uniquely identify a merchant transaction.
This value needs to be unique per merchant transaction, i.e. different merchants could use the same merchantTransactionReference for two different transactions but the value would need to be unique per transaction for a given merchant. In the event that the same merchantTransactionReference is supplied for two different transactions for the same merchant, the second transaction will be rejected by the Halo server, and the final transaction result type returned for the second transaction will be HaloTransactionResultType.DuplicateMerchantTransactionReferenceSupplied.
If the final transaction result type is HaloTransactionResultType.Indeterminate, the merchantTransactionReference should be used to look up and potentially resolve the final transaction outcome - potentially through a manual reversal by the merchant via the web portal (merchant portal).
The return type of startTransaction is HaloStartTransactionResult and is defined as:
public class HaloStartTransactionResult {
public HaloStartTransactionResultType resultType;
public HaloErrorCode errorCode;
}
where HaloStartTransactionResultType is:
public enum HaloStartTransactionResultType {
NotInitialized,
Started,
GeneralError,
NFCDisabledError,
RootedDevice,
InstrumentedDevice,
DebuggedDevice,
InvalidJWT,
UnableToActivateTerminal,
InvalidCurrency,
NoAppContext,
}
NotInitialized- The SDK has not been initialized, or the initialization failed.Started- The SDK is satisfied to start a new transaction.GeneralError- A general error occurred, the SDK is unable to start a transaction.NFCDisabledError- NFC is not enabled on the device, or the device does not support NFC.RootedDevice- The device is rooted, and the SDK cannot start a transaction.InstrumentedDevice- The device is running under instrumentation, and the SDK cannot start a transaction.DebuggedDevice- The device is running in debug mode, and the SDK cannot start a transaction.InvalidJWT- The JWT provided is invalid, or the SDK is unable to parse it.UnableToActivateTerminal- The SDK is unable to activate the terminal, typically due to a configuration issue or internal error.InvalidCurrency- The currency code provided is invalid.NoAppContext- The SDK is unable to start a transaction because the app context is not available, typically due to theonCreatemethod not being called.
Start Transaction Flow
As part of starting a transaction, the SDK will check:
- NFC is present and turned on
- SDK itself has been successfully initialized
- Platform runtime (root/debug/instrumentation)
HaloSDK.startTransaction will always synchronously return a HaloStartTransactionResultType, only a value of Started indicates that the SDK is satisfied to actually start a new transaction, all other values indicate a failure of some kind.
In the event of a failure, the return of the startTransaction method signals the end of the transaction and the Halo.SDK will invoke no further callbacks. This outcome should be regarded as the final outcome of this transaction, and full control returns to the mobile application (integrating app).
From this point onwards, in the event of a successful start, the Halo.SDK will communicate interim transaction progress back to the mobile application by means of invoking the IHaloCallback.onHaloUIMessage callback function, and the final transaction outcome by invoking the IHaloCallback.onHaloTransactionResult.
Informing the Merchant of a Tamper Event
If HaloSDK.startTransaction returns a result type of RootedDevice, InstrumentedDevice or DebuggedDevice, then the EMV specification dictates that it is mandatory for the host application to immediately inform the merchant on screen that their device has been tampered with.
Communication of Interim Status
Before the final transaction outcome is communicated via IHaloCallbacks.onHaloTransactionResult, interim transaction progress will typically be communicated to the mobile app via invoking IHaloCallbacks.onHaloUIMessage:
void onHaloUIMessage(HaloUIMessage message);
It is expected that the mobile app will use these message events as triggers for communicating interim transaction status information or action prompts such as present card, remove card, present card again to the card holder.
Let's have a closer look at HaloUIMessage:
import za.co.synthesis.halo.sdk.model.HaloUIMessage
public class HaloUIMessage {
public HaloUIMessageID msgID;
public int holdTimeMS;
public List<String> languagePreference;
public HaloCurrencyValue transactionAmount;
public HaloCurrencyValue offlineBalance;
}
And the parameters of HaloUIMessage:
-
HaloUIMessageID msgIDThe
msgIDfield indicates the interim transaction status, which should be communicated to the user. The following are the types thatmsgIDcan be:Enum Text Description PresentCard Present Card Initial message, accompanied by transaction amount Processing Processing... May occur between PresentCardandCardReadOK_RemoveCardCardReadOK_RemoveCard Card Read OK, Remove Card Card reading has been completed and user should remove card SeePhoneForInstructions_ThenTapAgain See Phone for Instructions, then Tap Again Authorise transaction on the payment device, then tap again AuthorisingWait Authorising, Please Wait... Attempting online authorization TryAgain Try Again Initial card read failed, cardholder to present card again - transaction still in progress TryAnotherCard Try Another Card Transaction failed, start a new transaction with a different card -
int holdTimeMSThe EMV terminal specification dictates that when multiple messages are received in quick succession for the same transaction, each message must be displayed for a minimum amount of time (the message hold time), before proceeeding to display the next message. This is intended to allow the user enough time to read each message, and typically results in queue-based implementations.
holdTimeMSreflects the message hold time, in units of milliseconds. -
List languagePreferenceThe EMV specification dictates that cards may include a list of language preferences. If the card does contain such a list, it will be specified inHaloUIMessageaslanguagePreference, which is a list of ISO 639-1 alpha2 language codes, in order of language.The mobile application can then choose to display the UI message texts in a preferred language, or if not specified, in its default language.
IHaloCallbacks.onHaloTransactionResult
Once a transaction has completed processing the Halo.SDK communicates the final transaction outcome to the mobile application (integrating app) via invoking the IHaloCallbacks.onHaloTransactionResult callback, and passing it a HaloTransactionResult object. Once the mobile application receives a HaloTransactionResult, it can regard the transaction as concluded, and assume full control again.
Here is a closer look at HaloTransactionResult:
public class HaloTransactionResult {
public HaloTransactionResultType resultType;
public String merchantTransactionReference;
public String haloTransactionReference;
public String paymentProviderReference;
public HaloErrorCode errorCode;
public List<String> errorDetails;
public HaloTransactionReceipt? receipt;
public Map<String, String>? customTags;
}
And the parameters of HaloTransactionResult:
-
HaloTransactionResultType resultTypeThe
HaloTransactionResultType resultTypefield indicates the final transaction status to the host application.Value Description Approved Transaction successfully approved online Declined Transaction declined, either offline by terminal or card, or online by issuer CardTapTimeOutExpired Timed out waiting for a card tap NetworkError Network socket communication error ProcessingError An error occurred during EMV card processing Cancelled Transaction cancelled by host application TryAnotherCard Transaction failed with this card, but may succeed with another card NFCDisabledError NFC on the device is turned off NotAuthenticated Invalid JWT token provided Indeterminate Unknown transaction status, inform merchant to manually query transaction status via merchant portal before giving goods DuplicateMerchantTransactionReferenceSupplied Transaction rejected by server due to use of duplicate merchant transaction reference. attempt again with a new reference HealthError An error occurred while checking the status of the Kernel Server InvalidJWT An error occurred while parsing the JWT DeveloperOptionsEnabled Developer options are enabled. Please turn them off and try again. Only if a
HaloTransactionResultTypeofApprovedis received should the merchant be instructed that the transaction has been successful. If a result of typeIndeterminateis returned, then the merchant MUST be instructed to query the Payment Processor as to the final transaction outcome - BEFORE giving goods/services. This will typically be done either through the host application itself, or via the payment processor's merchant management portal. All other values should be regarded as conclusively indicating that the transaction has failed. -
Transaction References
Reference Source merchantTransactionReference HaloSDK.startTransaction.merchantTransactionReferencehaloTransactionReference Halo server paymentProviderReference Payment Provider -
HaloTransactionReceipt
EMV receipt information is specified in
HaloTransactionResult.receipt. Approved transactions will always contain receipt information, whereas this is not guaranteed in the case of declined transactions.Field Description transactionDate Transaction Date, YYMMDD transactionTime Transaction Time, HHMMSS aid Application ID, 16 hex chars applicationLabel Application Label, 16 chars applicationPreferredName Application Preferred Name, 16 chars tvr Terminal Verification Results, 10 hex chars cvr Card Verification Results, hex cryptogramType Application Cryptogram type: AAC, TC, ARQC cryptogram Application Cryptogram, 16 hex chars maskedPAN Card PAN masked according to PCI, 16 chars authorizationCode The final authorization code returned by the issuer in the online response, 12 chars ISOResponseCode Authorisation Response Code returned by the issuer in the online response association Card scheme: MasterCard, Visa, AMEX expiryDate Card application expiry date mid Merchant Identifier for the payment provider used merchantName Merchant name tid Terminal identifier stan System Trace Audit Number panEntry PAN entry mode for the transaction cardType Card type e.g. Credit Card panSequenceNumber PAN sequence number effectiveDate Card effective date disposition Card application expiry date currencyCode Currency code amountAuthorised Amount authorised amountOther Additional amount -
Example HaloTransactionResult
onHaloTransactionResult: {
resultType: Approved,
merchantTransactionReference: 2d3c88e3-a100-4288-a902-87cb43031c37,
haloTransactionReference: a55dc97e-5d7a-48ae-b3d9-3e7a14b8be2e,
paymentProviderReference: 000000239368,
errorCode: 0,
customTags: {
resultCodeText: Approved,
originalIsoResponseCode: 00,
authorisedAmount: 369,
displayText: Successful Transaction,
receiptText: Card PAN ,
stan: 239368,
base24Time: 162804,
base24Date: 0901,
ICCData: 910ADB924439BA6E9C680012,
base24RespCode: 000,
additionalReceiptBodyText: ,
SignedTransaction: eyJhbGciOiJQUzUxMiJ9.eyJpc1NpbmdsZVRhcEFuZFBpbiI6ZmFsc2UsInR5cGUiOiJBcHByb3ZlZCIsImF1dGhvcml6YXRpb25Db2RlIjoiMTUyMDgwIiwidGFncyI6W10sImhhbG9SZWZlcmVuY2UiOiJhNTVkYzk3ZS01ZDdhLTQ4YWUtYjNkOS0zZTdhMTRiOGJlMmUiLCJlcnJvck1lc3NhZ2UiOiIiLCJpc29SZXNwb25zZUNvZGUiOiIwMCIsImFzc29jaWF0aW9uIjoiIiwiZXhwaXJ5RGF0ZSI6IiIsInBheW1lbnRQcm92aWRlclJlZmVyZW5jZSI6IjAwMDAwMDIzOTM2OCIsImN1c3RvbVZhbHVlcyI6eyJyZXN1bHRDb2RlVGV4dCI6IkFwcHJvdmVkIiwib3JpZ2luYWxJc29SZXNgdI6DRKkrzAuqxZsVcYM,
transactionTime: 142746,
applicationPreferredName: ,
cryptogramType: ARQC,
panSequenceNumber: 00,
cvr: 03A2000400,
amountAuthorised: 369,
cryptogram: 31AC1DDFC4528944,
serialisedReceipt: rO0ABXNyAD96YS5jby5zeW50aGVzaXMuaGFsby5oYWxvQ29tbW9uSW50ZXJmYWNlLkhhbG9UcmFu
c2FjdGlvblJlY2VpcHRadWGnlac5lgIAGkwAAWF0ABJMamF2YS9sYW5nL1N0cmluZztMAAFicQB+
AAFMAAFjcQB+AAFMAAFkcQB+AAFMAAFlcQB+AAFMAAFmcQB+AAFMAAFncQB+AAFMAAFodAA9THph
L2NvL3N5bnRoZXNpcy9oYWxvL2hhbG9Db21tb25JbnRlcmZhY2UvSGFsb0NyeXB0b2dyYW1UeXBl
O0wAAWlxAH4AAUwAAWpxAH4AAUwAAWtxAH4AAUwAAWxxAH4AAUwAAW1xAH4AAUwAAW5xAH4AAUwA
AW9xAH4AAUwAAXBxAH4AAUwAAXFxAH4AAUwAAXJxAH4AAUwAAXNxAH4AAUwAAXRxAH4AAUwAAXVx
AH4AAUwAAXZxAH4AAUwAAXdxAH4AAUwAAXh0ABZMamF2YS9tYXRoL0JpZ0ludGVnZXI7TAABeXEA
fgADTAABenEAfgADeHB0AAYyNTA5MDF0AAYxNDI3NDZ0AA5BMDAwMDAwMDA0MTAxMHQAEE1BU1RF
UkNBUkQgICAgICB0AAB0AAowMDAwMDA4MDAxdAAKMDNBMjAwMDQwMH5yADt6YS5jby5zeW50aGVz
aXMuaGFsby5oYWxvQ29tbW9uSW50ZXJmYWNlLkhhbG9DcnlwdG9ncmFtVHlwZQAAAAAAAAAAEgAA
eHIADmphdmEubGFuZy5FbnVtAAAAAAAAAAASAAB4cHQABEFSUUN0ABAzMUFDMURERkM0NTI4OTQ0
dAAQNTE4MTAzKioqKioqMzQyNXQABjE1MjA4MHQAAjAwdAAAdAAAcQB+AAlxAH4ACXEAfgAJdAAG
MjM5MzY4cQB+AAlxAH4ACXQAAjAwdAAGMjQwOTAxdAAIQXBwcm92ZWRzcgAUamF2YS5tYXRoLkJp
Z0ludGVnZXKM/J8fqTv7HQMABkkACGJpdENvdW50SQAJYml0TGVuZ3RoSQATZmlyc3ROb256ZXJv
Qnl0ZU51bUkADGxvd2VzdFNldEJpdEkABnNpZ251bVsACW1hZ25pdHVkZXQAAltCeHIAEGphdmEu
bGFuZy5OdW1iZXKGrJUdC5TgiwIAAHhwAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAF1cgACW0Ks8xf4BghU
4AIAAHhwAAAAAgLGeHNxAH4AGgAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABdXEAfgAeAAAAAgFxeHNxAH4A
GgAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAABdXEAfgAeAAAAAgFxeA==,
maskedPAN: 518103******3425,
ISOResponseCode: 00, cardType: ,
amountOther: 369,
transactionDate: 250901,
tvr: 0000008001,
disposition: Approved,
applicationLabel: MASTERCARD,
stan: 239368,
aid: A0000000041010,
currencyCode: 710,
effectiveDate: 240901
},
errorDetails: []
}
8. SDK Async Behaviour after startTransaction Returns
Assuming that startTransaction returns a synchronous result type of Started , the SDK will continue with async transaction processing.
Pre-Processing
The SDK will first perform transaction pre-processing as per the EMV specification. The transaction can be declined during pre-processing (typically due to terminal limits). In this case, the SDK will communicate this by calling IHaloCallbacks.onHaloTransactionResult with HaloTransactionResult.resultType as Declined, then terminate, sending no UI messages.
Enablement of NFC Field
Assuming that pre-processing succeeds, the SDK will attempt to turn the NFC field on. If it is not able to do so (typically because NFC has not been enabled within phone settings), then the SDK will abandon the transaction, and return HaloTransactionResult.resultType as NFCDisabledError.
Confirmation of Transaction Amount
Assuming that the NFC field could be enabled, the SDK will then send a PresentCard HaloUIMessageID, with the transaction amount specified in the transactionAmount field. No action is required by the user to confirm the amount, the message is displayed only for information purposes.
Wait for Tap or Timeout
At this point, the SDK will wait for either a card to be tapped, or for the card tap timeout to expire. If the timeout occurs, then the SDK will abandon the transaction, and return HaloTransactionResult.resultType as CardTapTimeOutExpired.
On Tap
Assuming the card is tapped in time, the SDK will engage with the card. At this point, 1 of 2 things can happen:
- A processing error, or decline occurs during the card interaction e.g.
HaloTransactionResult.resultTypeofProcessingErroris returned, and the SDK abandons transaction. - The card interaction completes successfully. In this case, the SDK will send a
CardReadOK_RemoveCardUI message, and continue with async transaction processing.
Potential for Offline Decline
Under some situations the attempted online transaction may be declined offline by the card and the SDK will return a HaloTransactionResult.resultType of Declined with an error code and abandon the transaction.
PIN
If the transaction amount exceeds the CVM limit and the card supports online PIN, the SDK will request a PIN for the transaction. This is handled transparently by the SDK using a Trusted User Interface, which will briefly assume control of the mobile device screen to capture a PIN.
Once the PIN has been captured control will return to the calling application. If a release version of the HaloSDK is used, this Trusted User Interface will not work on devices that have developer options enabled, or if there are apps with accessibility services installed on the device. In such an instance, the SDK will return error codes of 'DeveloperOptionsBlocksPin' or 'AccessibilityBlocksPin', respectively.
Online Processing
Assuming that the card interaction was successful, no processing errors were encountered, and that the card did not decline the transaction outright, then the SDK will attempt to prepare, submit and process an online transaction authorization request.
The SDK will send a AuthorisingWait UI message to indicate that is begun online processing.
General Error During Online Processing
If there is a general error during the preparation of the online request, the SDK will return a HaloTransactionResult.resultType of ProcessingError, and abandon the transaction.
Could Not go Online
If the SDK is unable to submit the online authorization request due to network connectivity issues, it will return a HaloTransactionResult.resultType of NetworkError, and abandon the transaction.
Ambiguous Transaction Outcome
In the event that the SDK was able to connect and submit an online authorization request, but did not receive a response, it will return a HaloTransactionResult.resultType of Indeterminate and abandon the transaction.
In this case, the SDK integrator must be instructed to consult the transaction back-end in order to determine the final transaction outcome before the merchant is able to hand over the goods/services sold.
Final Transaction Outcome
Once the SDK has received and processed the online response, it will communicate the final transaction outcome, which at this point should be one of Approved, Declined or NotAuthenticated. A result of NotAuthenticated typically means that the JWT supplied has expired, and that the transaction should be restarted with a fresh JWT. The SDK will then terminate the current transaction.
Try Another Card
In some cases the SDK will determine that the transaction cannot be completed with the current card/device, in this case it will return a TryAnotherCard result, and the mobile app should instruct the user to attempt the transaction with a different card. From the perspective of the SDK, this will be a new transaction.
Try Again Flow
In some unusual cases, the SDK will require the user to present the same card/device again, in order to complete the transaction. In these cases, the SDK will retain control, but will require the mobile application to communicate instructions to the user via ui messages during the transaction. These instructions will either be to tap the same card/device again ( TryAgain ), or to first consult their device for instructions (if paying with a digital wallet or emulated card e.g. Samsung Pay), then tap the device again ( SeePhoneForInstructions_ThenTapAgain ). It is only when the transaction has been finally concluded that the SDK will communicate a final transaction result as per normal, then terminate.
9. Integrating the Halo SDK in a Multi-Activity Kotlin Android App
Overview
This integration demonstrates how to structure a Halo SDK payment flow within an Android app that uses multiple Activity classes. The implementation covers:
- SDK initialization in an Application class
- Permission management and activity lifecycle callbacks in the Parent Activity
- Launching a payment flow via an Intent
- Handling callbacks and results in a custom IHaloCallbacks implementation
- Displaying transaction results in a dedicated success screen
Initialization and Application Context
The MyApplication class initializes the Halo SDK once per app session using the initializeHaloSdk() method.
class MyApplication: Application() {
var haloCallbacks: HaloCallbacks? = null
var isInitialized = false
fun initializeHaloSdk(activity: Activity) {
HaloSDK.onCreate(this, activity)
if (isInitialized) {
return
}
Thread {
val timer = Timer()
haloCallbacks = HaloCallbacks(this, activity, timer) {}
timer.start()
HaloSDK.initialize(
HaloInitializationParameters(
haloCallbacks,
60000,
applicationInfo.packageName,
BuildConfig.VERSION_NAME,
)
)
}.start()
}
}
An Application class is used so that the initialization state and callbacks can be shared across all activities. The SDK is initialized in a separate thread to avoid blocking the UI thread. This function, initializeHaloSdk(), should be called in your parent activity - where the payment methods are shown i.e.
// Initialize Halo SDK
if (requestNecessaryPermissions()) {
val app = application as MyApplication
app.initializeHaloSdk(this)
}
Permissions and Entry Point: Parent Activity
The Parent Activity, in this case MainActivity, requests camera and Bluetooth permissions. On success, it initializes the Halo SDK and provides a button to trigger a transaction.
val intent = Intent(this, PayActivity::class.java).apply {
putExtra("transactionId", "sometransactionId")
putExtra("transactionAmount", "100")
}
startActivity(intent)
Starting a Transaction
On navigation to the PayActivity, the following occurs:
- UI elements like amount are updated.
- HaloSDK.onCreate() is called again with this new Activity context.
- HaloSDK.startTransaction() is called with the amount and transaction ID passed via Intent.
This isolates transaction logic in a dedicated screen, simplifying the user experience.
Handling Callbacks: IHaloCallbacks
HaloCallbacks extends IHaloCallbacks and contains detailed logic for:
- Initialization: Verifies result, logs errors, and triggers onInitializationSuccess.
- Transaction Results: Parses and displays transaction results.
- JWT: Uses JwtToken to sign and pass a JWT using RSA keys.
- Health and security monitoring: Handles attestation and verification events.
override fun onHaloTransactionResult(result: HaloTransactionResult) {
val intent = Intent(activity, TransactionSuccess::class.java).apply {
putExtra("TRANSACTION_ID", result.merchantTransactionReference)
putExtra("CARD_NUMBER", result.receipt?.maskedPAN.toString())
...
}
activity.startActivity(intent)
PayActivity.currentInstance?.get()?.finish()
}
Route to an activity to display a receipt for your user.
For the full source code, visit: https://github.com/halo-dot/test_app-android_sdk
10. Conclusion
That concludes the guide to integrating the Halo.SDK into your application. For any questions, please do not hesitate to reach out to the Halo Dot Team.
Not what you were looking for? If you are looking for the Intent Integration guide, it is over here